Biotin vs Collagen: What’s the Difference?
Biotin vs collagen: two essential nutrients that play crucial roles in maintaining overall health and well-being. Biotin, a B-vitamin, supports healthy hair, skin, and nails, while collagen, the most abundant protein in the body, is essential for maintaining the integrity of connective tissues like skin, bones, and joints. These nutrients have gained popularity as supplements due to their significant health benefits.
In addition to promoting external beauty, supplements like biotin and collagen, similar to bone broth supplements, which are rich in collagen and support joint and skin health. Incorporating these into your routine can provide a natural collagen boost, promoting stronger bones, better skin elasticity, and improved overall well-being.
In this article, we’ll explore the differences between biotin and collagen, their benefits, dietary sources, and recommended intake levels to help you make informed decisions about supporting your health.
Key Article Findings:

What Is Biotin?
Biotin, also known as Vitamin B7, is a water-soluble B-vitamin essential for the body’s metabolic processes. It acts as a coenzyme, helping metabolize carbohydrates, fats, and proteins, which converts food into energy. Biotin plays a key role in maintaining healthy hair, skin, and nails by supporting the production of keratin, a crucial protein for these tissues.
Biotin can be obtained from foods like egg yolks, nuts, seeds, legumes, and vegetables such as sweet potatoes and spinach. It is also available in convenient supplement forms, including capsules and tablets.
Biotin Benefits
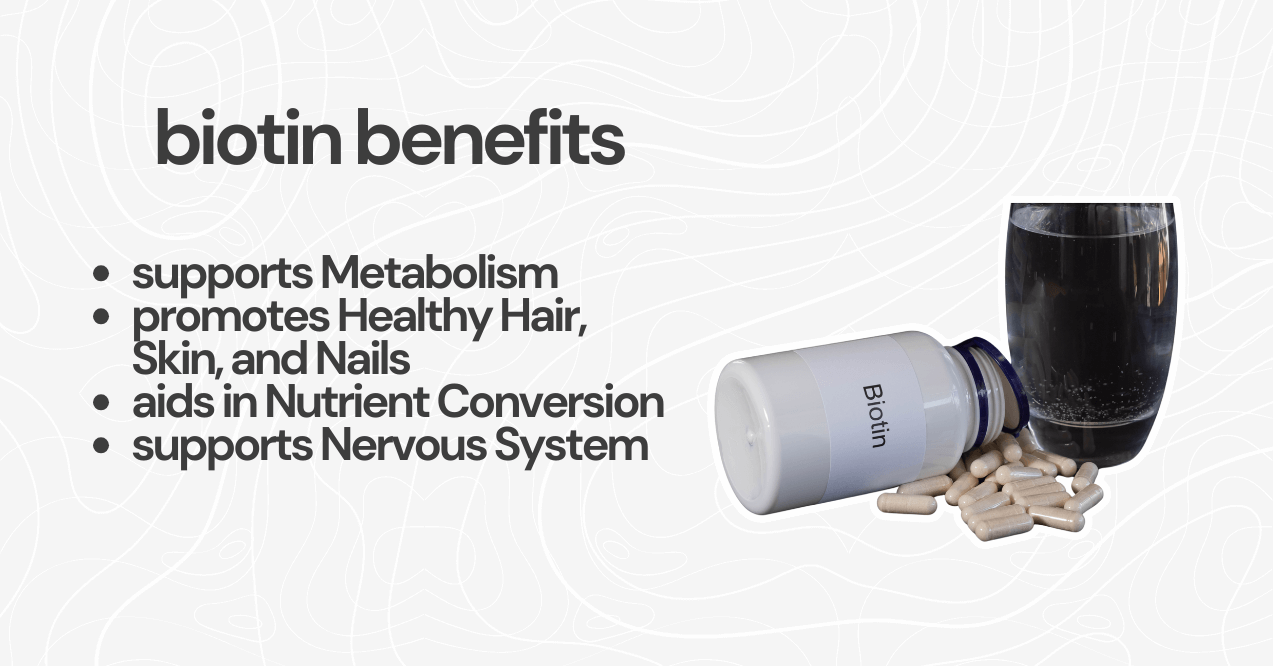
The benefits of biotin are broad, impacting multiple aspects of health and wellness. Some of the key benefits of biotin include:
- Supports Metabolism – Biotin plays a crucial role in metabolizing carbohydrates, fats, and proteins, which is essential for energy production.
- Promotes Healthy Hair, Skin, and Nails – It is well-known for its role in maintaining the strength, resilience, and appearance of hair and skin.
- Aids in Nutrient Conversion – Biotin also helps convert various nutrients into energy, ensuring that the body can efficiently use the food ingested.
- Supports Nervous System – Biotin is involved in nerve signaling, which helps maintain the health of the nervous system.
What Is Collagen?
Collagen is the most abundant protein in the body, making up about one-third of its total protein composition. It provides structural support and strength to tissues like skin, bones, joints, tendons, and ligaments.
There are several types of collagen, with Types I, II, and III being the most common. Type I is found in skin, bones, and tendons; Type II is in cartilage; and Type III is abundant in skin, muscles, and blood vessels.
As we age, collagen production decreases, leading to signs of aging like wrinkles, sagging skin, and joint discomfort. Maintaining healthy collagen levels is key to preserving skin elasticity, supporting joint health, and ensuring tissue integrity.
Collagen Benefits

Collagen offers numerous health benefits, owing to its structural and functional roles in the body. Some of the key benefits of collagen include:
- Supports Skin Health – Collagen is a major component of the skin, providing elasticity, hydration, and reducing the appearance of wrinkles and fine lines.
- Promotes Joint Comfort – As a key structural component of cartilage, collagen helps maintain joint health and supports joint comfort and mobility.
- Contributes to Bone Strength – Collagen is essential for maintaining bone density and strength, helping to prevent age-related bone loss.
- Supports Hair and Nail Health – Collagen provides the building blocks for keratin production, promoting healthy hair and nails.
- Aids in Gut Health – Collagen helps maintain the integrity of the digestive tract lining, supporting overall gut health.
Biotin vs Collagen
Biotin vs Collagen: While both nutrients are essential for overall health, they serve distinct roles in the body. Biotin, a B-vitamin, supports metabolic processes, converting nutrients into energy, and helps maintain the health of hair, skin, and nails. In contrast, collagen is a structural protein that provides support and elasticity to tissues such as skin, bones, and joints.
Studies by D.P. Patel et al. (2020) show that biotin supplementation can improve hair thickness and reduce nail brittleness, making it a popular choice for those looking to enhance hair and nail health.
Collagen, however, is primarily focused on maintaining skin elasticity, reducing wrinkles, and supporting joint health. Research by L. Bolke et al. (2022) revealed that collagen supplements can reduce joint discomfort and improve skin hydration and elasticity.
While biotin boosts energy and supports cellular function, collagen strengthens connective tissues and promotes youthful skin. Understanding biotin vs collagen can help individuals select the right supplement to meet their specific health needs.
Similarities
Biotin vs collagen, although different in their primary functions, share some similarities in their contributions to overall health and well-being:
- Support for Hair, Skin, and Nails – Both biotin and collagen support the health of hair, skin, and nails. Biotin aids in keratin production, while collagen provides amino acids for keratin and maintains skin elasticity and hydration.
- Dietary Sources – Biotin and collagen can be obtained through various dietary sources. Biotin is found in foods such as egg yolks, nuts, seeds, and certain vegetables, while collagen is present in bone broth, meat, fish, and poultry.
- Supplementation – Both biotin and collagen vitamins can be obtained through dietary sources or supplements, depending on individual needs and preferences.
Differences
Despite their similarities, the difference between biotin and collagen is significant in their roles and functions within the body:
- Classification – Biotin is a water-soluble B-vitamin, while collagen is a structural protein. This fundamental difference in their classification underlies their unique roles and mechanisms of action in the body.
- Primary Functions – Biotin primarily supports metabolic processes and energy production, while collagen mainly provides structural support and strength to various tissues.
- Impact on Hair, Skin, and Nails – Although both contribute to hair, skin, and nail health, biotin directly supports keratin production, while collagen provides building blocks for keratin and maintains skin elasticity and hydration.
- Joint Health – Collagen has a more significant impact on joint health compared to biotin, as it is a key component of cartilage, maintaining joint comfort and mobility.
- Specific Health Benefits – Biotin supports the nervous system and glucose metabolism, while collagen benefits bone density, gut health, and wound healing, highlighting their unique roles in the body.
What Foods Are High In Collagen And Biotin?
While supplements are popular, obtaining biotin and collagen from food sources is beneficial for overall health. Consuming these nutrients through a balanced fast metabolism diet can provide additional vitamins to boost metabolism and minerals that support their absorption and effectiveness.
Collagen Food Sources

- Bone Broth – Made by simmering animal bones and connective tissues, bone broth is a rich source of collagen. It also provides amino acids, minerals, and compounds that support joint and gut health. How much collagen is in bone broth? While it varies, typically, bone broth can contain up to 10 grams of collagen per cup, making it a potent source. Additionally, for those wondering whether you can take collagen and bone broth together? The answer is yes. Combining these can enhance collagen intake, supporting skin, joints, and overall health.
- Chicken Skin – Chicken skin is rich in type I collagen, the most abundant collagen type in the body. Eating chicken skin can help boost collagen levels and support skin elasticity and joint health.
- Fish with Skin – Fish, especially when consumed with the skin, provides type I collagen. Fish skin also contains omega-3 fatty acids, which have anti-inflammatory properties.
- Gelatin – Derived from collagen, gelatin is used in many culinary applications and provides a concentrated source of collagen. It can help support skin hydration and joint health.
Biotin Food Sources

- Eggs (particularly egg yolks) – Egg yolks are one of the richest sources of biotin. They also contain essential fatty acids and proteins that support overall health.
- Nuts and Seeds – Almonds, sunflower seeds, and walnuts are excellent sources of biotin. They also provide healthy fats, fiber, and antioxidants.
- Avocados: Avocados are high in biotin and healthy monounsaturated fats, which support skin and heart health.
- Certain Meats – Organ meats like liver are exceptionally high in biotin. They also provide iron, vitamin A, and other essential nutrients.
For those seeking a convenient and potent source of collagen, trumeta bone broth protein Is an excellent choice. This product is made from high-quality, grass-fed beef bones, ensuring a rich supply of collagen types I and III. Each serving delivers a significant dose of collagen, alongside essential amino acids like glycine and proline, which support joint health, skin elasticity, and gut integrity.
Bone broth protein is free from artificial additives, gluten, and dairy, making it suitable for various dietary needs. It also contains naturally occurring minerals like calcium, magnesium, and phosphorus, which further support bone and overall health. The protein powder is easy to incorporate into your daily routine—simply mix it with water, smoothies, or recipes for a collagen boost.

By choosing trumeta bone broth protein, you can efficiently augment your collagen intake, supporting your body’s structural health and enhancing your wellness regimen.
Recommended Daily Intake of Biotin And Collagen
The recommended daily intake of biotin varies based on factors such as age, sex, and health conditions. For adults, the adequate intake (AI) is 30 micrograms per day. Pregnant and breastfeeding women may require slightly higher amounts. Although excessive biotin intake is rare, it can lead to skin rashes or digestive issues.
For collagen, daily intake typically ranges from 2.5 to 15 grams, depending on individual health goals. Higher doses are generally used to support joint and skin health. While collagen supplements are considered safe, excessive intake may cause digestive discomfort.
It’s always a good idea to consult with a healthcare provider before starting any new supplement regimen, particularly if you have existing health conditions or are on other medications. This ensures you get personalized recommendations and avoid potential side effects.
Conclusion
In the biotin vs collagen debate, both nutrients play unique roles in supporting overall health. Biotin helps maintain healthy hair, skin, and nails, while collagen is essential for skin elasticity, joint health, and tissue integrity.
Both can be obtained from foods like eggs, nuts, and bone broth. The recommended daily intake for biotin is 30 micrograms, while collagen ranges from 2.5 to 15 grams. Always consult with a healthcare provider before starting supplements to avoid side effects.
Understanding biotin vs collagen helps you make informed decisions to enhance your health and wellness.
yes, you can take biotin and collagen together. Both support different aspects of health, such as skin, hair, nails, and joints, and there are no known adverse interactions between them when taken simultaneously.
biotin is better known for directly supporting hair growth by enhancing keratin production. However, collagen also contributes by providing amino acids that support hair structure. Both can be beneficial, but biotin is specifically linked to promoting hair growth.
no, biotin is not the same as collagen. Biotin is a B-vitamin (Vitamin B7) that supports metabolic processes and hair, skin, and nail health. Collagen is a protein that provides structural support to skin, bones, and joints.
Advertisement. This site offers health, wellness, fitness and nutritional information and is designed for educational purposes only. You should not rely on this information as a substitute for, nor does it replace, professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. If you have any concerns or questions about your health, you should always consult with a physician or other health-care professional. Do not disregard, avoid or delay obtaining medical or health related advice from your health-care professional because of something you may have read on this site. The use of any information provided on this site is solely at your own risk.







