The 5 Best Natural Foods With Creatine
If you’re looking to boost your muscle energy and athletic performance, one of the best ways to do so is by incorporating foods with creatine supplements into your diet. Creatine is a naturally occurring compound found in muscle cells and plays a crucial role in producing energy during high-intensity activities like weightlifting or sprinting. It is widely known for its ability to support muscle strength, endurance, and exercise performance.
While many athletes use creatine supplements, you can also obtain this compound from various natural food sources, providing a balanced, nutrient-rich approach to enhancing your energy levels and physical capabilities. However, if you choose supplements, you might wonder, does creatine expire? Ensuring the quality and potency of your creatine can make a difference in achieving optimal results. Additionally, some individuals report experiencing a creatine headache after supplementation, which may be linked to hydration levels or dosage. Understanding these factors is key to maximizing the benefits of creatine while minimizing potential side effects.
Equally important to your performance and overall health is maintaining a healthy gut. Consuming the worst foods for gut health, such as highly processed foods, excessive sugar, and artificial additives, can harm your digestive system and interfere with nutrient absorption. A compromised gut may reduce your body’s efficiency in utilizing creatine and other nutrients essential for athletic performance. To optimize your results, consider focusing on gut-friendly foods like fiber-rich fruits, fermented products, and whole grains, alongside your creatine-rich diet.
Key takeaways:

How Can I Get Creatine Naturally?
Many people wonder if foods with creatine can provide the same benefits as supplements, and the answer is yes. Creatine is naturally present in animal-based proteins, making it easy to incorporate into your daily meals. By choosing natural sources of creatine like beef, fish, and poultry, you not only support your muscle energy but also benefit from the vitamins and nutrients these foods offer.
Does creatine make you bloated when consumed from natural sources? While some people experience bloating when taking creatine supplements, this is less likely when getting creatine from food. Natural creatine from whole foods is absorbed more gradually, helping to support energy levels without unwanted side effects. Plus, it’s a more holistic approach to fueling your body and enhancing your athletic performance.
Best Natural Foods with Creatine
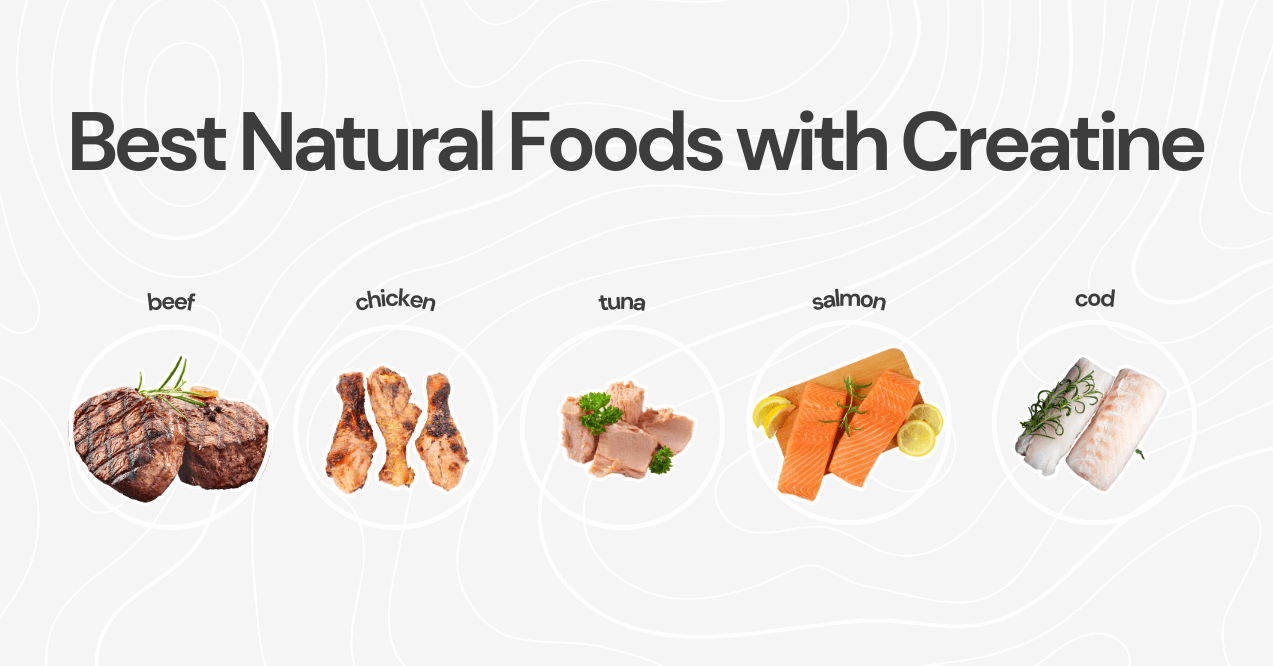
Understanding what foods have creatine allows you to naturally maintain optimal levels without relying on supplements, which can be a more sustainable approach for long-term health and fitness. Whole foods deliver creatine gradually, supporting muscle function without disrupting intermittent fasting goals or causing digestive discomfort.
Additionally, for those following specific dietary routines, a common question may arise: Does creatine break a fast? While creatine from supplements might raise concerns for some, obtaining it from natural food sources ensures you’re fueling your body in a balanced way that complements various nutritional approaches.
1. Beef
Beef is one of the richest natural sources of creatine, making it an excellent choice for anyone looking to boost their intake. A typical serving of steak or ground beef can provide a significant amount of creatine, which helps fuel your muscles during high-intensity activities.
In addition to creatine, beef is packed with high-quality protein, essential for muscle repair and growth. It also contains vital nutrients like iron, zinc, and B vitamins, all of which contribute to overall health and energy metabolism.
2. Tuna
For those wondering how to get creatine naturally, tuna can be a great option. This lean fish is not only rich in creatine but also provides an excellent source of high-quality protein. Both fresh and canned tuna are good options, making it easy to include in your diet. Tuna is also known for being rich in omega-3 fatty acids, which support heart health, and it offers a convenient way to maintain creatine levels without extra fat or calories.
3. Chicken
Chicken, especially chicken breast, is one of the best food sources of creatine. It’s a lean protein that’s widely available and easy to incorporate into a variety of meals. A typical serving of chicken breast provides a moderate amount of creatine, which helps maintain muscle energy. In addition to its creatine content, chicken is low in fat and packed with protein, making it a favorite among athletes and health-conscious individuals.
The versatility of chicken makes it ideal for many recipes, from grilled chicken salads to stir-fries, ensuring you can enjoy its benefits without getting bored of the same meal. Whether roasted, baked, or sautéed, chicken offers a nutrient-dense way to support your creatine intake.
4. Cod
Cod is another excellent source of creatine, particularly for those seeking foods high in creatine but low in fat. As a lean, white fish, cod offers a good amount of creatine while being low in calories and saturated fat. It’s perfect for those aiming to boost creatine intake without extra calories.
Cod can be prepared in various ways, such as baking, grilling, or poaching, making it a versatile option for health-conscious meals. Along with creatine, cod is rich in vitamins B6 and B12, which are essential for energy production and maintaining a healthy nervous system.
5. Salmon
Salmon stands out not only for its creatine content but also for its abundance of omega-3 fatty acids. Omega-3s are well-known for supporting heart health, reducing inflammation, and promoting brain function. Whether grilled, smoked, or baked, salmon is a flavorful and nutritious option that enhances your diet with both creatine and healthy fats. It’s an excellent way to maintain energy levels and support overall health while benefiting from this fatty fish. Salmon’s rich nutrient profile makes it a powerhouse food for athletes and health enthusiasts alike.
How Much Creatine Do You Need?
The recommended daily intake of creatine typically ranges from 1 to 3 grams[10] per day. However, individual needs can vary depending on several factors, including age, activity level, and muscle mass. Athletes or individuals engaged in high-intensity training may require higher amounts of creatine to support muscle energy and recovery. On the other hand, those with lower activity levels may not need as much.
Muscle mass also plays a role – people with more muscle tissue naturally store more creatine, which could increase their dietary requirements. Additionally, older adults may benefit from slightly higher creatine intake to support muscle maintenance as part of healthy aging. It’s important to adjust your creatine intake based on your unique lifestyle and goals, whether you’re getting creatine from food or supplements, to ensure optimal muscle performance and energy production.
If you find it challenging to obtain enough creatine from food sources alone or need an extra boost to support your fitness goals, Trumeta Creatine is a great solution. Made with 100% Creapure®, the purest form of creatine, Trumeta ensures you’re getting high-quality creatine without fillers.
While foods like beef, chicken, and fish provide natural creatine, a supplement like trumeta creatine can help you consistently meet your daily creatine needs, especially during intense workouts or when looking to enhance both muscle and cognitive performance. It’s a convenient, ultra-pure option for those seeking additional support.

Conclusion
Foods with creatine are an excellent way to naturally support muscle energy and overall performance. By incorporating options like beef, chicken, tuna, cod, and salmon into your diet, you can meet your daily creatine needs without relying on supplements. These foods not only provide creatine but also offer additional nutrients like protein, vitamins, and omega-3 fatty acids.
Depending on your activity level, age, and muscle mass, your creatine requirements may vary, but these natural sources can help ensure you’re fueling your body effectively to promote strength and endurance.
Foods that are high in creatine include beef, tuna, chicken, cod, and salmon. These animal-based proteins naturally boost creatine levels, supporting muscle energy, endurance, and recovery, making them excellent additions to a balanced diet.
Water itself doesn’t increase creatine levels, but staying hydrated is essential for creatine’s effectiveness. Adequate water intake helps transport creatine to muscles, improving its absorption and supporting muscle function during high-intensity activities or workouts.
Cooking can slightly reduce the creatine content in foods, but most of it remains intact. While high-heat cooking methods may cause some loss, foods like beef and fish still provide valuable creatine even after being cooked.
Advertisement. This site offers health, wellness, fitness and nutritional information and is designed for educational purposes only. You should not rely on this information as a substitute for, nor does it replace, professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. If you have any concerns or questions about your health, you should always consult with a physician or other health-care professional. Do not disregard, avoid or delay obtaining medical or health related advice from your health-care professional because of something you may have read on this site. The use of any information provided on this site is solely at your own risk.