What Is a Metabolic Workout? 7 Effective Exercises for Women
If you ever wondered what is a metabolic workout? Search no further! Want a workout that torches calories, revs up your metabolism, and sculpts your body all at once? Welcome to the world of metabolic training!
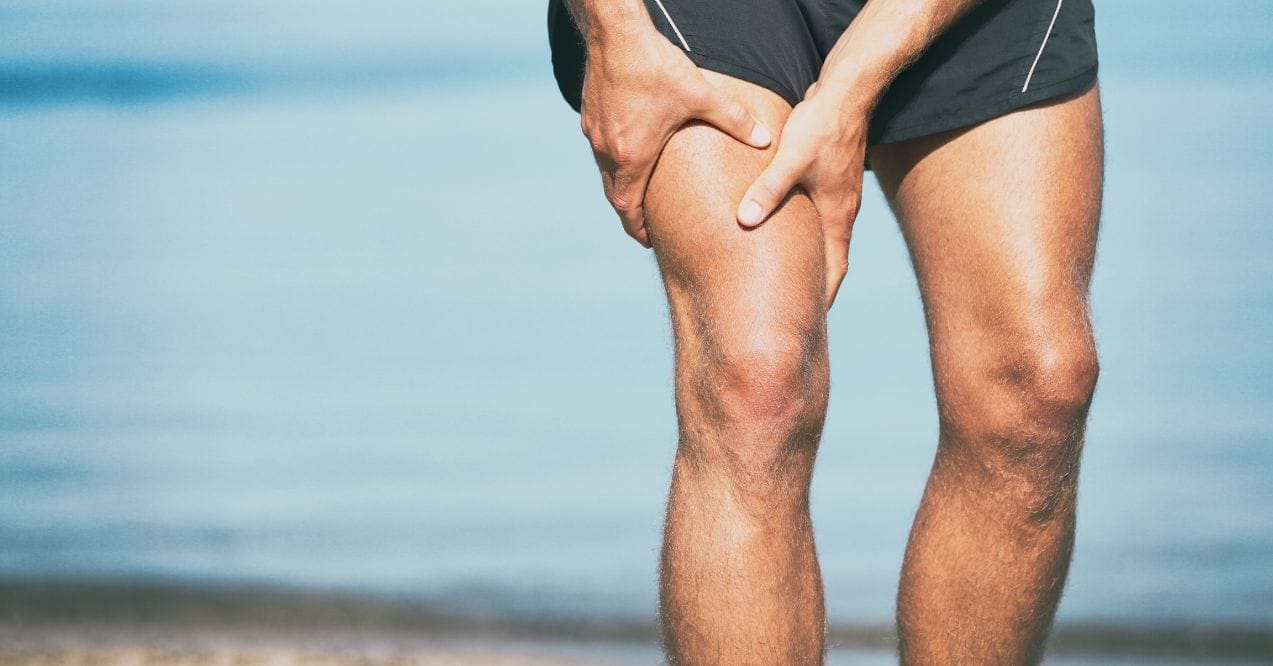
This isn’t your average gym routine. These high-intensity workouts engage multiple muscle groups in every move, keeping your body burning fat long after you’ve finished. You might notice bloating after a workout, which can happen due to rapid breathing, dehydration, or your body’s natural recovery process. The good news is, with the right hydration and recovery, this bloating tends to pass quickly, leaving you feeling stronger and more energized.
To enhance your metabolic workouts, incorporating performance supplements can be a game-changer. These supplements are designed to fuel your body, improving endurance, recovery, and overall performance during your training sessions. For those focusing on building strength and size, adding a muscle gain stack—featuring key supplements like protein, creatine, and amino acids—can amplify your results by helping you maximize muscle growth and recovery.
If you’re ready to transform your fitness and achieve your goals faster, you’re in the right place. For those who are looking for a more relaxed training routine we suggest checking out our somatic workout plan.
Now, Let’s dive into the exciting world of metabolic workouts!
Key takeaways:

What Is a Metabolic Workout?
It’s a special kind of workout designed to boost your metabolism, which is the process your body uses to convert food into energy. But how do metabolic workouts and metabolic exercises work exactly?
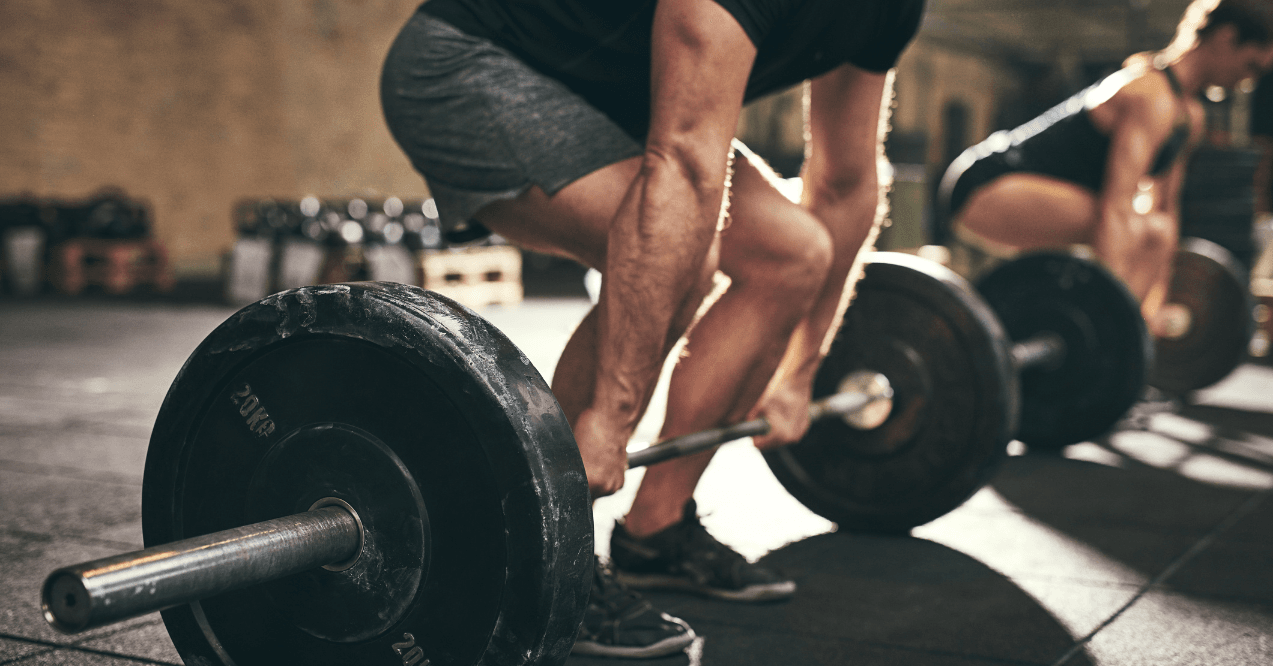
- Cardio and Strength – These workouts are a powerful blend of cardiovascular exercise and strength training, maximizing calorie burn and building muscle simultaneously.
- Intense Bursts and Short Rests – Metabolic workouts involve short periods of high-intensity exercise followed by brief rest periods. This format keeps your heart rate elevated, leading to increased calorie burn both during and after your workout.
- Compound Movements – A typical metabolic workout includes compound exercises like squats, lunges, push-ups, and rows. These moves engage multiple muscle groups at once, making your workout more efficient and effective.
Pro Tip: Feeling the burn after an intense metabolic workout? Kickstart your recovery with Trumeta Recovery. Whether you’re battling “next day” soreness, replenishing lost electrolytes, or fighting fatigue, Trumeta Recovery has you covered. This powerful blend of ingredients helps minimize muscle damage, improves energy and focus! No more groggy starts – just revitalized energy and the motivation to tackle your next challenge.
Metabolic Workout for Beginners
- Start with shorter circuits of 3-4 exercises. Keeping the circuits brief allows you to focus on proper form and build up your endurance gradually.
- Perform each exercise for 30-45 seconds. This time frame provides an intense burst of activity without overwhelming your body.
- Rest for 15-30 seconds between exercises. These short rest intervals allow you to catch your breath while keeping your heart rate elevated.
- Aim for 2-3 rounds. Completing multiple rounds will increase the overall challenge and calorie burn.
- Gradually increase intensity and duration as you progress. As you become more comfortable with metabolic training, you can increase the intensity by adding more exercises, extending the work intervals, or reducing rest periods.
- Aim for 2-3 metabolic sessions per week. Consistency is key for seeing results, but be sure to allow adequate recovery time between sessions.
Metabolic Workout for Intermediates
- Increase the number of exercises to 5-6 per circuit. Adding more exercises will challenge your endurance and engage multiple muscle groups.
- Extend work intervals to 45-60 seconds. Longer work intervals will increase the cardiovascular and muscular demands of the workout.
- Incorporate challenging variations like dumbbells or resistance bands. Using external resistance will increase the intensity and promote muscle growth.
- Aim for 3-4 rounds. Completing multiple rounds will amplify the overall calorie burn and metabolic challenge.
- Reduce rest periods to 15-20 seconds. Shorter rest intervals will keep your heart rate elevated and maximize the cardiovascular benefits.
Metabolic Workout for Advanced
- Combine 6-8 exercises into a high-intensity circuit. More exercises will create a comprehensive, full-body challenge.
- Work intervals ranging from 60-90 seconds. Longer work intervals will test your muscular endurance and cardiovascular fitness.
- Incorporate plyometric movements like jump squats or lateral lunges. Explosive exercises will increase the intensity and promote power development.
- Challenge your power and endurance with explosive exercises. Plyometric movements will elevate your heart rate and demand more energy expenditure.
- Aim for 4-5 rounds. Multiple rounds will ensure a substantial calorie burn and metabolic boost.
- Minimal rest periods of 10-15 seconds. Short rest intervals will keep your body working at a high intensity throughout the workout.
Three Advantages of Metabolic Workouts
1. Building Muscle
- Compound exercises work multiple muscle groups simultaneously
- High intensity promotes muscular development and functional strength
- Elevated heart rate increases circulation flow and oxygen delivery to muscles
2. Broad Spectrum Exercise
- Target upper body, lower body, and core in a single session
- Functional movements like burpees and mountain climbers challenge overall athleticism
- Customizable to focus on specific goals or muscle groups
- Well-rounded approach ensures no muscle group is neglected
3. Fat Burning
- High-intensity intervals keep heart rate elevated for maximum calorie expenditure
- Combination of resistance and cardio exercises torches more calories than steady-state cardio
- “Afterburn” effect (EPOC) means you continue burning calories after the workout
- Rev up your metabolism for hours, promoting around-the-clock fat burning
- Consistent metabolic training leads to a leaner, more sculpted physique
Some people may experience bloating after workout sessions, especially if they consume food or drinks too close to their training. To minimize this discomfort, aim to have a light meal 1-2 hours before your metabolic workout and stay hydrated with water throughout the day.
Seven Most Effective Exercises for Women

While the science behind metabolic workouts is the same for everyone, there are some unique considerations for women.
Metabolic workouts for women might include very specific exercises. Want to sculpt those glutes, carve out a strong core, or define your arms? We’ve got you covered with targeted exercises that fit right into your metabolic routine.
So, are you ready to sweat? Here are seven of the most effective metabolic exercises you can include in your metabolic workouts for women:
1. Mountain Climbers
How to Do It
- Start in a high plank position with your hands directly under your shoulders.
- Engage your core and bring one knee towards your chest, then quickly switch legs, driving your other knee towards your chest.
- Continue alternating legs in a rapid, climbing motion.
Benefits
- Full-body calorie-burning move that engages your core, shoulders, and legs
- Improves overall cardiovascular fitness and endurance, which can be further supported by incorporating the best supplements for endurance into your routine.
2. Burpees
How to Do It
- Start standing, then drop into a squat position with your hands on the floor.
- Kick your feet back into a plank position, then immediately reverse the motion by jumping your feet back towards your hands.
- Finish by jumping vertically with your arms overhead.
Benefits
- Challenges every major muscle group for total-body strengthening
- Elevates heart rate rapidly, providing an intense cardiovascular challenge that can be sustained with the help of the best supplements for endurance.
3. Kettlebell Swings
How to Do It
- Stand with your feet shoulder-width apart, holding a kettlebell with both hands.
- Hinge at the hips to swing the kettlebell back between your legs
- Then explosively drive through your heels to swing the weight forward and up to chest height.
Benefits
- Dynamic exercise that ignites your posterior chain (back, glutes, hamstrings)
- Builds power and sculpts a toned backside.
4. Lunge Switch Jumps
How to Do It
- Start in a lunge position with one leg forward.
- Jump up, switching leg positions mid-air, landing with the opposite leg forward.
- Continue alternating legs with each explosive jump.
Benefits
- Combines leg-toning benefits of lunges with plyometric power
- Targets quads, glutes, and cardiovascular fitness.
5. Lateral Lunges
How to Do It
- Stand with your feet shoulder-width apart, then step out to one side, lowering your hips and bending your knee.
- Push through your heel to return to the starting position, then repeat on the other side.
Benefits
- Sculpts inner and outer thighs for toned, defined legs
- Challenges balance and stability for improved athleticism.
6. Plank Jacks
How to Do It
- Start in a high plank position, then jump your feet out and in, mimicking the motion of a jumping jack while keeping your upper body stable in a plank.
Benefits
- Engages your entire core for a strong, toned midsection
- Dynamic leg movements elevate heart rate for cardiovascular benefits.
7. Jump Squat
How to Do It
- Stand with your feet shoulder-width apart.
- Then send your hips back and bend your knees to lower into a squat position.
- Explosively push through your heels to jump vertically, extending your hips and legs fully.
Benefits
- Combines strength-building benefits of squats with explosive plyometric power
- Targets quads, glutes, and overall athleticism for a functionally fit physique.
Conclusion
In summary, metabolic workouts are a powerhouse of fitness, blending cardio and strength training to maximize calorie burn, build muscle, and sculpt a lean, strong physique. With intense bursts of compound movements like burpees, kettlebell swings, and jump squats, these workouts engage multiple muscles, boost cardio endurance, and target key areas like the core, legs, and glutes. Beginners can ease in with shorter circuits and fewer rounds, while intermediate and advanced exercisers can push their limits with longer intervals and additional exercises. Whether you’re aiming to tone, build power, or enhance overall fitness, metabolic workouts offer an effective, full-body approach to achieving your goals.
Metabolic workouts typically last 20-30 minutes. They consist of high-intensity intervals followed by short rest periods. The duration varies based on fitness level, with beginners starting with shorter circuits and advanced exercisers increasing the length of work intervals and number of rounds.
Yes, metabolic workouts are excellent for effective weight management. The high-intensity intervals burn significant calories during the workout, while the “afterburn” effect (EPOC) keeps metabolism elevated for hours afterward. This combination of intense calorie burning and a revved-up metabolism promotes fat loss and helps achieve a leaner physique.
Metabolic meals are designed to support metabolic health and weight management goals. They typically include lean proteins, complex carbohydrates, and healthy fats in balanced portions. The goal is to provide the body with the nutrients it needs while keeping calorie intake in check to promote fat loss.
Advertisement. This site offers health, wellness, fitness and nutritional information and is designed for educational purposes only. You should not rely on this information as a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. If you have any concerns or questions about your health, you should always consult with a physician or other health-care professional. Do not disregard, avoid or delay obtaining medical or health related advice from your health-care professional because of something you May have read on this site. The use of any information provided on this site is solely at your own risk.
Advertisement. This site offers health, wellness, fitness and nutritional information and is designed for educational purposes only. You should not rely on this information as a substitute for, nor does it replace, professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. If you have any concerns or questions about your health, you should always consult with a physician or other health-care professional. Do not disregard, avoid or delay obtaining medical or health related advice from your health-care professional because of something you may have read on this site. The use of any information provided on this site is solely at your own risk.







